Describe What Surface Tension Is Using Kinetic-molecular Theory
Evaporati on Only at the surface Boiling Vaporizati on Through all the liquid At any temperature At the boiling point. ADescribe all the phase changes a sample of solid water would undergo when heated to its critical temperature at a pressure of 100 atm.
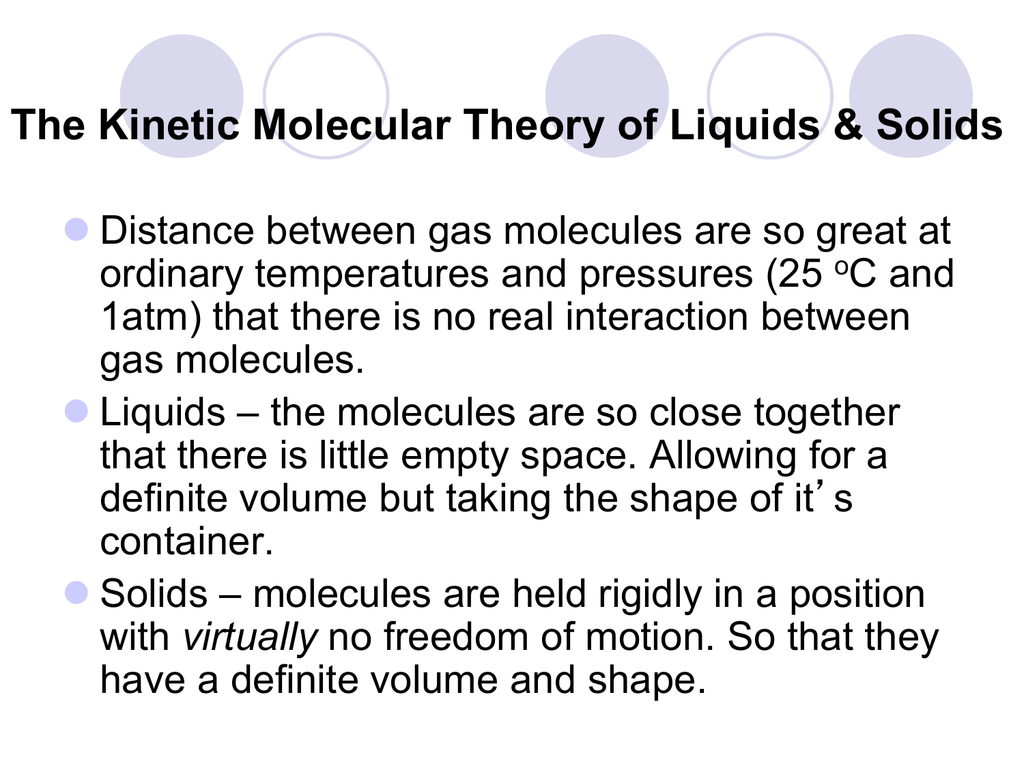
The Kinetic Molecular Theory Of Liquids Solids
37g of glucose C6H1205 in 64g of water Use the editor to format your answer.

. This in turn determines whether the substance exists in the solid liquid or gaseous state. Select all that apply. The kinetic-molecular theory explains the physical properties of solids liquids and gases in terms of the energy of particles and the.
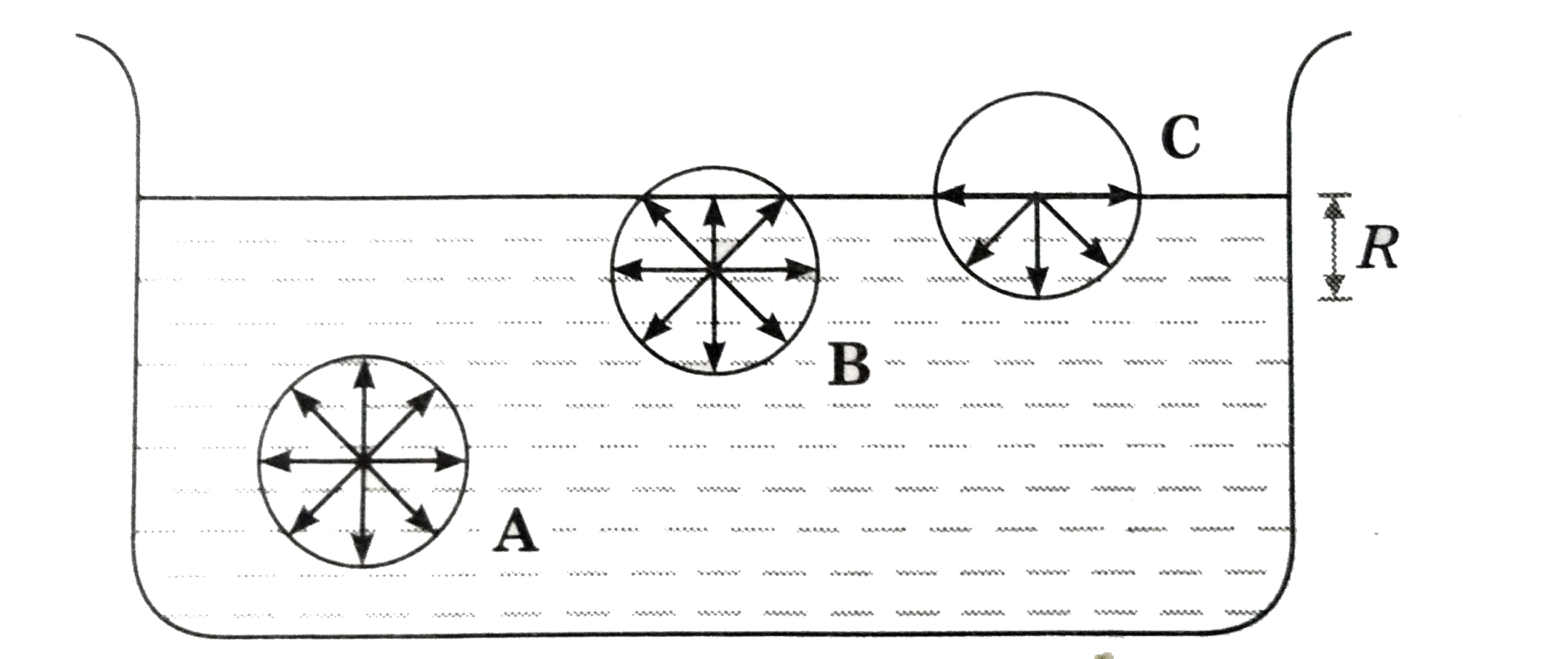
Are far apart b. 1Kinetic Molecular Theory states that gas particles are in constant motion and exhibit perfectly elastic collisions. The force that pulls the outer layer of a liquids surface together reducing its surface area to the smallest possible size Describe the liquid state according to the kinetic-molecular theory.
Kinetic Molecular Theory of Liquids and Solids ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS. Use the kinetic theory of matter to describe the properties of matter. Identify each statement as True or False.
This can lead to interesting properties such as the ability of certain objects to float on the surface of a liquid even if they are denser than that liquid. Surface tension a force that tends to pull adjacent parts of a liquids surface together thereby decreasing surface area to the smallest possible size capillary action. Describe the Gas state according to the kinetic-molecular theory.
Using gas kinetic molecular theory show that under typical atmospheric conditions of pressure and temperature corresponding to an altitude of 5 km see Appendix V collisional deactivation of a CO 2 molecule will be much faster than reemission of the absorbed radiation. Explain the nature of liquid and solid states using the kinetic molecular theory 2. According to the kinetic-molecular theory of liquids the particles are not bound together in fixed positions.
The average kinetic energy of a collection of gas particles is directly proportional to absolute temperature only. All matter is made up of tiny particles. Surface tension is a property of liquids that makes it slightly more favorable for a liquid to minimize its surface area.
The speed of particle is proportional to temperature. Less intermolecular forces holding them They overcome the attraction forces that hold them to the surface and escape to the gaseous state. Kinetic Molecular Theory can be used to explain both Charles and Boyles Laws.
All particles have energy but the energy varies depending on the temperature the sample of matter is in. Move rapidly in a constant random motion d. What factors determine the physical properties of substance.
Matter is made up of particles that are constantly moving. How do molecular forces affect surface tension. 4What does the negative slope of waters solidliquid equilibrium line indicate.
Select all that apply. Kinetic Molecular Theory can be used to explain both Charles and Boyles Laws. Which of the following options correctly describe the phases of matter in terms of kinetic molecular theory.
Have a significant volume with respect to the volume of the container they occupy c. According to the basic assumption of kinetic molecular theory gas particles. Gas particles are in constant line motion so they move until they make contact with a wall of a container.
Instead they move about constantly giving them their fluidity List the properties of liquids. Kinetic Molecular Theory states that gas particles are in constant motion and exhibit perfectly elastic collisions. 1- Liquids have a high density relative to gases.
The Kinetic-Molecular Theory Explains the Behavior of Gases Part I Recalling that gas pressure is exerted by rapidly moving gas molecules and depends directly on the number of molecules hitting a unit area of the wall per unit of time we see that the KMT conceptually explains the behavior of a gas as follows. Check all that apply The particles of a liquid have enough kinetic energy to move randomly past each other allowing the liquid to flow. Concept Notes 101 Ch 101 Reading Assessment.
Describe Kinetic Molecular Theory. Explain the difference between an ideal gas and a real gas and under what conditions they exist. Liquid particles at the surface have higher kinetic energies and move faster.
The average amount of empty space between molecules gets progressively larger as a sample of matter. Using the Kinetic Molecular theory explain the observed volatility or ease of evaporation of some liquids such as alcohol and gasoline especially at elevated temperature conditions-The kinetic molecular theory of matter states that. What is surface tension.
Define an ideal gas. These are particles are in constant motion. Using the kinetic molecular theory explain why a gas can be easily compressed while a liquid and a solid cannot.
Use the editor to format your answer 1 Point Question 3 Describe the 4 standards that gases need to have in order to fit the kinetic molecular theory of gases. Molecular theory of surface tension. The average kinetic energy of a collection of gas particles is directly proportional to absolute temperature only.
At the end of the lesson you should be able to. Lose kinetic energy when colliding 4. The Kinetic Molecular Theory explains the properties of solids and liquids in terms of intermolecular forces of attraction and the kinetic energy of the individual particles.
Attractive forces of the molecules create surface tension. Describe the motion of gas particles in an ideal gas. Take the collision diameter to be 0456 nm and the radiative lifetime of the 15-μm band of CO 2 to be 074 s.
The kinetic molecular theory of matter states that. Why iscarbon dioxides positive. Describe kinetic molecular theory.
Their density is about 1000 x that of the gas of the same substance. Use the editor to format your answer Paint Question 23 Calculate the molality of the following solution. -definite volume -takes shape of its container.
What are the characteristics that distinguish solids liquids and gases.

Section 1 The Kinetic Molecular Theory Of Matter Ppt Download
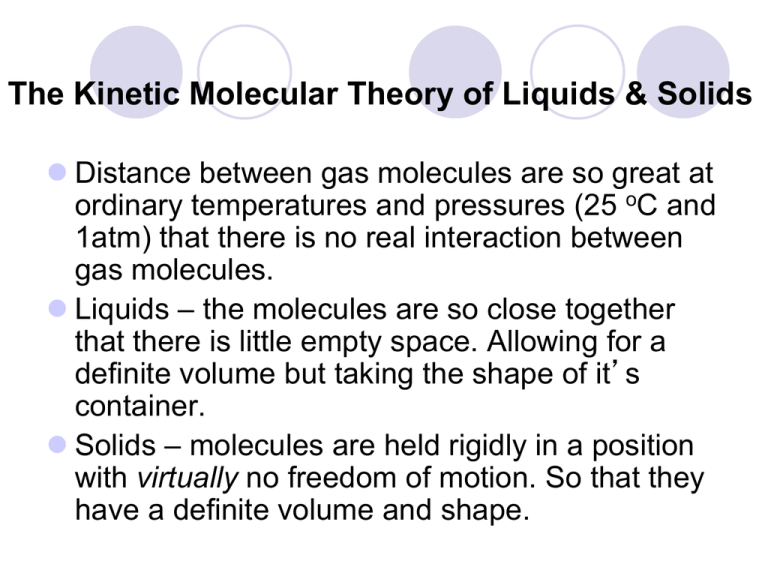
The Kinetic Molecular Theory Of Liquids Solids

Explain Surface Tension On The Basis Of Molecular Theory Brainly In

The Kinetic Molecular Theory Of Liquids Solids Ppt Video Online Download

Explain The Phenomenon Of Surface Tension On The Basis Molecular Theory
Surface Tension The Concept Its Characteristics And Factors Affecting It
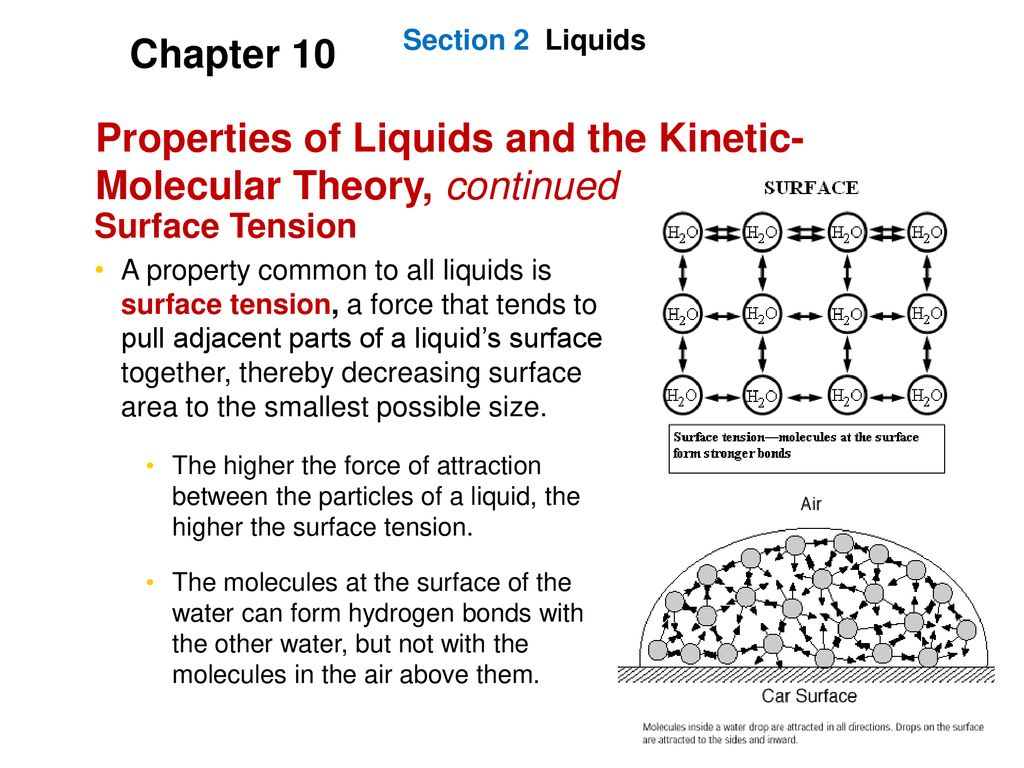
The Kinetic Molecular Theory Of Gases Ppt Download

Explanation Of Surface Tension By Laplace S Molecular Theory Qs Study

The Kinetic Molecular Theory Of Gases Ppt Download
Explanation Of Surface Tension By Laplace S Molecular Theory Qs Study
Explain The Phenomenon Of Surface Tension On The Basis Molecular Theory

Ch 10 Kinetic Molecular Theory Notes

The Kinetic Molecular Theory Of Gases Ppt Download

Chapter 10 Notes The Kinetic Molecular Theory Is Based On

The Kinetic Molecular Theory Of Gases Ppt Download

Pdf Molecular Theory Of Surface Tension

Chemistry Kinetic Molecular Theory States Of Matter Chapter Ppt Download


Comments
Post a Comment